Easy Methods To Treat Pes Planus
Overview
Flat Feet and Fallen Arches are terms used to describe feet that have a low or no arch when weight bearing. There are two types of Flat Feet. Rigid Flat Foot. This type of foot is structurally flat, therefore, it has the same appearance when weight bearing and non weight bearing. Flexible Flat Foot. This is where the arch is present when non-weight bearing; however, when weight bearing it falls or collapses to a flat foot. This foot type is commonly referred to as Fallen Arches. Both of these foot types may be asymptomatic; however, they are characterised by excessive pronation of the joints of the foot (commonly the subtalar joint). The forces associated with this excessive pronation commonly results in pathological conditions, such as plantar fasciitis and tibialis posterior dysfunction which may cause pain in the feet.
Causes
Aging, injury, overuse, or illness can result in fallen arches or a fallen arch on one side. Diabetes. Obesity. Pregnancy. Nerve conditions. Foot abnormalities present since birth. Broken or dislocated bones in the foot. Stretched or torn tendons. Medical conditions such as arthritis. Sudden weight gain
Symptoms
Some people have fallen arches, and they aren?t even aware of it, fallen arches are sometimes asymptomatic and do not always cause pain. However, for others, the following symptoms may be present. Foot pain, particularly in the arches or heels, leg or back pain, feet feel tired quickly, swelling in the feet and difficulty moving the feet.
Diagnosis
You can always give yourself the ?wet test? described above to see whether you have flat feet. Most people who do not notice their flat feet or have no pain associated with them do not think to see a foot doctor. Flat feet can lead to additional problems such as stiffness or pain, however, especially if the condition appears out of nowhere. If you think you may have flat feet, you should seek medical attention to ensure there are no additional issues to worry about. Your doctor will be able to diagnose you with a number of tests. For example, he or she may have you walk around, stand still, or stand on your tiptoes while you are being examined. Your doctor may also examine your foot?s shape and functionality. It?s important to let your foot doctor know about your medical and family history. In some cases, your doctor may order imaging tests such as x-rays or an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to determine a cause of your flat foot. If tarsal coalition is suspected in children, a CT scan is often ordered.
deelsonheels
Non Surgical Treatment
Flexible flat feet that are painless do not require treatment. If you have pain due to flexible flat feet, an orthotic (arch-supporting insert in the shoe) can bring relief. With the increased interest in running, many shoe stores carry shoes for normal feet and pronated feet. The shoes designed for pronated feet make long distance running easier and less tiring because they correct for the abnormality. Rigid or painful flat feet require evaluation by a health care provider. The treatment depends on the cause of the flat feet. For tarsal coalition, treatment starts with rest and possibly a cast. If this fails to improve the pain, surgery may be necessary. For problems with the posterior tibial tendon, treatment may start with rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and shoe inserts or ankle braces. In more advanced cases, surgery may be needed to clean or repair the tendon, or fuse some of the joints of the foot into a corrected position. Flat feet in older adults can be treated with pain relievers, orthotics, and sometimes surgery.
Surgical Treatment

In cases of flat feet that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required and in some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the best approach for you.
Prevention
oll away pain. If you're feeling pain in the arch area, you can get some relief by massaging the bottom of your foot. A regular massage while you're watching TV can do wonders" Stretch out. Doing the same type of stretching exercises that runners do in their warm-up can help reduce arch pain caused by a tight heel cord. One of the best exercises is to stand about three feet from a wall and place your hands on the wall. Leaning toward the wall, bring one foot forward and bend the knee so that the calf muscles of the other leg stretch. Then switch legs. Stretching is particularly important for women who spend all week in heels and then wear exercise shoes or sneakers on weekends. Get measured each time you buy new shoes. Don't assume that since you always wore a particular size, you always will. Too many people try to squeeze into their 'regular' shoe size and wind up with serious foot problems or sores on their feet. When your arch is falling, your feet may get longer or wider and you may or may not feel pain, so getting your foot measured each time you buy shoes is a good indicator of your arch's degeneration. Examine your shoes. If the heel is worn down, replace it. But if the back portion of the shoe is distorted or bent to one side, get yourself into a new pair of supportive shoes like those made specifically for walking. That's because flat feet can affect your walking stride, and failing to replace worn shoes may lead to knee or hip pain.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.

Flat Feet and Fallen Arches are terms used to describe feet that have a low or no arch when weight bearing. There are two types of Flat Feet. Rigid Flat Foot. This type of foot is structurally flat, therefore, it has the same appearance when weight bearing and non weight bearing. Flexible Flat Foot. This is where the arch is present when non-weight bearing; however, when weight bearing it falls or collapses to a flat foot. This foot type is commonly referred to as Fallen Arches. Both of these foot types may be asymptomatic; however, they are characterised by excessive pronation of the joints of the foot (commonly the subtalar joint). The forces associated with this excessive pronation commonly results in pathological conditions, such as plantar fasciitis and tibialis posterior dysfunction which may cause pain in the feet.
Causes
Aging, injury, overuse, or illness can result in fallen arches or a fallen arch on one side. Diabetes. Obesity. Pregnancy. Nerve conditions. Foot abnormalities present since birth. Broken or dislocated bones in the foot. Stretched or torn tendons. Medical conditions such as arthritis. Sudden weight gain
Symptoms
Some people have fallen arches, and they aren?t even aware of it, fallen arches are sometimes asymptomatic and do not always cause pain. However, for others, the following symptoms may be present. Foot pain, particularly in the arches or heels, leg or back pain, feet feel tired quickly, swelling in the feet and difficulty moving the feet.
Diagnosis
You can always give yourself the ?wet test? described above to see whether you have flat feet. Most people who do not notice their flat feet or have no pain associated with them do not think to see a foot doctor. Flat feet can lead to additional problems such as stiffness or pain, however, especially if the condition appears out of nowhere. If you think you may have flat feet, you should seek medical attention to ensure there are no additional issues to worry about. Your doctor will be able to diagnose you with a number of tests. For example, he or she may have you walk around, stand still, or stand on your tiptoes while you are being examined. Your doctor may also examine your foot?s shape and functionality. It?s important to let your foot doctor know about your medical and family history. In some cases, your doctor may order imaging tests such as x-rays or an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to determine a cause of your flat foot. If tarsal coalition is suspected in children, a CT scan is often ordered.
deelsonheels
Non Surgical Treatment
Flexible flat feet that are painless do not require treatment. If you have pain due to flexible flat feet, an orthotic (arch-supporting insert in the shoe) can bring relief. With the increased interest in running, many shoe stores carry shoes for normal feet and pronated feet. The shoes designed for pronated feet make long distance running easier and less tiring because they correct for the abnormality. Rigid or painful flat feet require evaluation by a health care provider. The treatment depends on the cause of the flat feet. For tarsal coalition, treatment starts with rest and possibly a cast. If this fails to improve the pain, surgery may be necessary. For problems with the posterior tibial tendon, treatment may start with rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and shoe inserts or ankle braces. In more advanced cases, surgery may be needed to clean or repair the tendon, or fuse some of the joints of the foot into a corrected position. Flat feet in older adults can be treated with pain relievers, orthotics, and sometimes surgery.
Surgical Treatment

In cases of flat feet that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required and in some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the best approach for you.
Prevention
oll away pain. If you're feeling pain in the arch area, you can get some relief by massaging the bottom of your foot. A regular massage while you're watching TV can do wonders" Stretch out. Doing the same type of stretching exercises that runners do in their warm-up can help reduce arch pain caused by a tight heel cord. One of the best exercises is to stand about three feet from a wall and place your hands on the wall. Leaning toward the wall, bring one foot forward and bend the knee so that the calf muscles of the other leg stretch. Then switch legs. Stretching is particularly important for women who spend all week in heels and then wear exercise shoes or sneakers on weekends. Get measured each time you buy new shoes. Don't assume that since you always wore a particular size, you always will. Too many people try to squeeze into their 'regular' shoe size and wind up with serious foot problems or sores on their feet. When your arch is falling, your feet may get longer or wider and you may or may not feel pain, so getting your foot measured each time you buy shoes is a good indicator of your arch's degeneration. Examine your shoes. If the heel is worn down, replace it. But if the back portion of the shoe is distorted or bent to one side, get yourself into a new pair of supportive shoes like those made specifically for walking. That's because flat feet can affect your walking stride, and failing to replace worn shoes may lead to knee or hip pain.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.
Leg Length Discrepancy Special Test
Overview
Approximately 75% of us present with one leg longer than the other. It?s staggering, literally, that so many people walk about with an imbalance. Yet to have one leg longer than the other doesn?t seem to create pain for everyone but for those that it does it brings pain in a myriad of dysfunction from TMJ, headaches, low back pain, IBS, bladder problems, sexual dysfunction, sacroiliac joint pain, pubis dysfunction, groin strain, gluteal dysfunction as well as the formation of trigger points.
Causes
Some children are born with absence or underdeveloped bones in the lower limbs e.g., congenital hemimelia. Others have a condition called hemihypertrophy that causes one side of the body to grow faster than the other. Sometimes, increased blood flow to one limb (as in a hemangioma or blood vessel tumor) stimulates growth to the limb. In other cases, injury or infection involving the epiphyseal plate (growth plate) of the femur or tibia inhibits or stops altogether the growth of the bone. Fractures healing in an overlapped position, even if the epiphyseal plate is not involved, can also cause limb length discrepancy. Neuromuscular problems like polio can also cause profound discrepancies, but thankfully, uncommon. Lastly, Wilms? tumor of the kidney in a child can cause hypertrophy of the lower limb on the same side. It is therefore important in a young child with hemihypertrophy to have an abdominal ultrasound exam done to rule out Wilms? tumor. It is important to distinguish true leg length discrepancy from apparent leg length discrepancy. Apparent discrepancy is due to an instability of the hip, that allows the proximal femur to migrate proximally, or due to an adduction or abduction contracture of the hip that causes pelvic obliquity, so that one hip is higher than the other. When the patient stands, it gives the impression of leg length discrepancy, when the problem is actually in the hip.
Symptoms
As patients develop LLD, they will naturally and even unknowingly attempt to compensate for the difference between their two legs by either bending the longer leg excessively or standing on the toes of the short leg. When walking, they are forced to step down on one side and thrust upwards on the other side, which leads to a gait pattern with an abnormal up and down motion. For many patients, especially adolescents, the appearance of their gait may be more personally troublesome than any symptoms that arise or any true functional deficiency. Over time, standing on one's toes can create a contracture at the ankle, in which the calf muscle becomes abnormally contracted, a condition that can help an LLD patient with walking, but may later require surgical repair. If substantial enough, LLD left untreated can contribute to other serious orthopaedic problems, such as degenerative arthritis, scoliosis, or lower back pain. However, with proper treatment, children with leg length discrepancy generally do quite well, without lingering functional or cosmetic deficiencies.
Diagnosis
The evaluation of leg length discrepancy typically involves sequential x-rays to measure the exact discrepancy, while following its progression. In addition, an x-ray of the wrist allows us to more carefully age your child. Skeletal age and chronological age do not necessarily equal each other and frequently a child's bone age will be significantly different than his or her stated age. Your child's physician can establish a treatment plan once all the facts are known: the bone age, the exact amount of discrepancy, and the cause, if it can be identified.
Non Surgical Treatment
For minor limb length discrepancy in patients with no deformity, treatment may not be necessary. Because the risks may outweigh the benefits, surgical treatment to equalize leg lengths is usually not recommended if the difference is less than 1 inch. For these small differences, the physician may recommend a shoe lift. A lift fitted to the shoe can often improve walking and running, as well as relieve any back pain that may be caused by the limb length discrepancy. Shoe lifts are inexpensive and can be removed if they are not effective.

what happens if one leg is shorter than the other?
Surgical Treatment
Many people undergo surgery for various reasons - arthritis, knee replacement, hip replacement, even back surgery. However, the underlying cause of leg length inequality still remains. So after expensive and painful surgery, follow by time-consuming and painful rehab, the true culprit still remains. Resuming normal activities only continues to place undue stress on the already overloaded side. Sadly so, years down the road more surgeries are recommended for other joints that now endure the excessive forces.
Approximately 75% of us present with one leg longer than the other. It?s staggering, literally, that so many people walk about with an imbalance. Yet to have one leg longer than the other doesn?t seem to create pain for everyone but for those that it does it brings pain in a myriad of dysfunction from TMJ, headaches, low back pain, IBS, bladder problems, sexual dysfunction, sacroiliac joint pain, pubis dysfunction, groin strain, gluteal dysfunction as well as the formation of trigger points.

Causes
Some children are born with absence or underdeveloped bones in the lower limbs e.g., congenital hemimelia. Others have a condition called hemihypertrophy that causes one side of the body to grow faster than the other. Sometimes, increased blood flow to one limb (as in a hemangioma or blood vessel tumor) stimulates growth to the limb. In other cases, injury or infection involving the epiphyseal plate (growth plate) of the femur or tibia inhibits or stops altogether the growth of the bone. Fractures healing in an overlapped position, even if the epiphyseal plate is not involved, can also cause limb length discrepancy. Neuromuscular problems like polio can also cause profound discrepancies, but thankfully, uncommon. Lastly, Wilms? tumor of the kidney in a child can cause hypertrophy of the lower limb on the same side. It is therefore important in a young child with hemihypertrophy to have an abdominal ultrasound exam done to rule out Wilms? tumor. It is important to distinguish true leg length discrepancy from apparent leg length discrepancy. Apparent discrepancy is due to an instability of the hip, that allows the proximal femur to migrate proximally, or due to an adduction or abduction contracture of the hip that causes pelvic obliquity, so that one hip is higher than the other. When the patient stands, it gives the impression of leg length discrepancy, when the problem is actually in the hip.
Symptoms
As patients develop LLD, they will naturally and even unknowingly attempt to compensate for the difference between their two legs by either bending the longer leg excessively or standing on the toes of the short leg. When walking, they are forced to step down on one side and thrust upwards on the other side, which leads to a gait pattern with an abnormal up and down motion. For many patients, especially adolescents, the appearance of their gait may be more personally troublesome than any symptoms that arise or any true functional deficiency. Over time, standing on one's toes can create a contracture at the ankle, in which the calf muscle becomes abnormally contracted, a condition that can help an LLD patient with walking, but may later require surgical repair. If substantial enough, LLD left untreated can contribute to other serious orthopaedic problems, such as degenerative arthritis, scoliosis, or lower back pain. However, with proper treatment, children with leg length discrepancy generally do quite well, without lingering functional or cosmetic deficiencies.
Diagnosis
The evaluation of leg length discrepancy typically involves sequential x-rays to measure the exact discrepancy, while following its progression. In addition, an x-ray of the wrist allows us to more carefully age your child. Skeletal age and chronological age do not necessarily equal each other and frequently a child's bone age will be significantly different than his or her stated age. Your child's physician can establish a treatment plan once all the facts are known: the bone age, the exact amount of discrepancy, and the cause, if it can be identified.
Non Surgical Treatment
For minor limb length discrepancy in patients with no deformity, treatment may not be necessary. Because the risks may outweigh the benefits, surgical treatment to equalize leg lengths is usually not recommended if the difference is less than 1 inch. For these small differences, the physician may recommend a shoe lift. A lift fitted to the shoe can often improve walking and running, as well as relieve any back pain that may be caused by the limb length discrepancy. Shoe lifts are inexpensive and can be removed if they are not effective.

what happens if one leg is shorter than the other?
Surgical Treatment
Many people undergo surgery for various reasons - arthritis, knee replacement, hip replacement, even back surgery. However, the underlying cause of leg length inequality still remains. So after expensive and painful surgery, follow by time-consuming and painful rehab, the true culprit still remains. Resuming normal activities only continues to place undue stress on the already overloaded side. Sadly so, years down the road more surgeries are recommended for other joints that now endure the excessive forces.
Everything You Will Need To Understand About
Overview

Heel pain is one of the most common conditions treated by podiatrists. It is often a message that something is in need of medical attention. Pain that occurs right after an injury or early in an illness may play a protective role, often warning us about the damage we have suffered. Heel pain is a problem which affects people of all ages and vocations, whether they are active or not and it comes in many different forms. Heel pain can also occur in children usually between the ages of 8 and 13, as they become increasingly active in sporting activities and during the growing phase.
Causes
Heel pain can have many causes but the vast majority is caused by plantar fasciitis. Plantar means, ?bottom of the foot.? Fascia is a ligament or ?bundle? of ligaments. The plantar fascia is the thick ligament that helps to hold up the foot and provide spring in our step. Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the plantar fascia and causes more than 90% of heel pain among adults in the US. Plantar fasciitis can be acute, that is, as simple strain of the ligament but often is chronic, hanging on for months if not years. Why does that happen? The answer is poor foot mechanics, the foot sinking down too far allowing the plantar fascia to overstretch with each step taken.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain along the inside edge of the heel near the arch of the foot. The pain is worse when weight is placed on the foot especially after a long period of rest or inactivity. This is usually most pronounced in the morning when the foot is first placed on the floor. This symptom called first-step pain is typical of plantar fasciitis. Prolonged standing can also increase the painful symptoms. It may feel better after activity but most patients report increased pain by the end of the day. Pressing on this part of the heel causes tenderness. Pulling the toes back toward the face can be very painful.
Diagnosis
A biomechanical exam by your podiatrist will help reveal these abnormalities and in turn resolve the cause of plantar fasciitis. By addressing this cause, the patient can be offered a podiatric long-term solution to his problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
Calf stretch, Heel cups/lifts, ice, night splint, physical therapy, activity modification. Sometimes immobilization in a cast or boot may be necessary. Topical creams, such as Voltaren or Ketoprofen, have been found to have some benefit. In some cases, the tendon may become degenerative (tendonosis). In these instances, treatment is more difficult. Prolonged periods of immobilization and physical therapy may be required. In resistant cases, surgical debridement of the tendon may be necessary. Rarely does a symptomatic achilles tendon rupture. Most achilles ruptures are not associated with prodromal symptoms. Achilles ruptures are more common in men and "weekend warriors," ie middle aged men who like to play sports (soccer, softball, basketball) on the weekends.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery to correct heel pain is generally only recommended if orthotic treatment has failed. There are some exceptions to this course of treatment and it is up to you and your doctor to determine the most appropriate course of treatment. Following surgical treatment to correct heel pain the patient will generally have to continue the use of orthotics. The surgery does not correct the cause of the heel pain. The surgery will eliminate the pain but the process that caused the pain will continue without the use of orthotics. If orthotics have been prescribed prior to surgery they generally do not have to be remade.
heel cups for heel pain
Prevention

It may not be possible to prevent all cases of heel pain. However, there are some easy steps that you can take to avoid injury to the heel and prevent pain. Whenever possible, you should wear shoes that fit properly and support the foot, wear the right shoes for physical activity, stretch your muscles before exercising, pace yourself during physical activity, maintain a healthy diet, rest when you feel tired or when your muscles ache, maintain a healthy weight.

Heel pain is one of the most common conditions treated by podiatrists. It is often a message that something is in need of medical attention. Pain that occurs right after an injury or early in an illness may play a protective role, often warning us about the damage we have suffered. Heel pain is a problem which affects people of all ages and vocations, whether they are active or not and it comes in many different forms. Heel pain can also occur in children usually between the ages of 8 and 13, as they become increasingly active in sporting activities and during the growing phase.
Causes
Heel pain can have many causes but the vast majority is caused by plantar fasciitis. Plantar means, ?bottom of the foot.? Fascia is a ligament or ?bundle? of ligaments. The plantar fascia is the thick ligament that helps to hold up the foot and provide spring in our step. Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the plantar fascia and causes more than 90% of heel pain among adults in the US. Plantar fasciitis can be acute, that is, as simple strain of the ligament but often is chronic, hanging on for months if not years. Why does that happen? The answer is poor foot mechanics, the foot sinking down too far allowing the plantar fascia to overstretch with each step taken.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain along the inside edge of the heel near the arch of the foot. The pain is worse when weight is placed on the foot especially after a long period of rest or inactivity. This is usually most pronounced in the morning when the foot is first placed on the floor. This symptom called first-step pain is typical of plantar fasciitis. Prolonged standing can also increase the painful symptoms. It may feel better after activity but most patients report increased pain by the end of the day. Pressing on this part of the heel causes tenderness. Pulling the toes back toward the face can be very painful.
Diagnosis
A biomechanical exam by your podiatrist will help reveal these abnormalities and in turn resolve the cause of plantar fasciitis. By addressing this cause, the patient can be offered a podiatric long-term solution to his problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
Calf stretch, Heel cups/lifts, ice, night splint, physical therapy, activity modification. Sometimes immobilization in a cast or boot may be necessary. Topical creams, such as Voltaren or Ketoprofen, have been found to have some benefit. In some cases, the tendon may become degenerative (tendonosis). In these instances, treatment is more difficult. Prolonged periods of immobilization and physical therapy may be required. In resistant cases, surgical debridement of the tendon may be necessary. Rarely does a symptomatic achilles tendon rupture. Most achilles ruptures are not associated with prodromal symptoms. Achilles ruptures are more common in men and "weekend warriors," ie middle aged men who like to play sports (soccer, softball, basketball) on the weekends.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery to correct heel pain is generally only recommended if orthotic treatment has failed. There are some exceptions to this course of treatment and it is up to you and your doctor to determine the most appropriate course of treatment. Following surgical treatment to correct heel pain the patient will generally have to continue the use of orthotics. The surgery does not correct the cause of the heel pain. The surgery will eliminate the pain but the process that caused the pain will continue without the use of orthotics. If orthotics have been prescribed prior to surgery they generally do not have to be remade.
heel cups for heel pain
Prevention

It may not be possible to prevent all cases of heel pain. However, there are some easy steps that you can take to avoid injury to the heel and prevent pain. Whenever possible, you should wear shoes that fit properly and support the foot, wear the right shoes for physical activity, stretch your muscles before exercising, pace yourself during physical activity, maintain a healthy diet, rest when you feel tired or when your muscles ache, maintain a healthy weight.
Mortons Neuroma Diagnosis
Overview
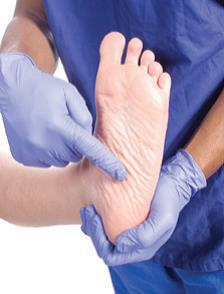
.jpg) Morton?s neuroma occurs as the nerve passes under the ligament connecting the toe bones (metatarsals) in the forefoot. Morton?s neuroma most frequently develops between the third and fourth toes, usually in response to irritation, trauma or excessive pressure. The incidence of Morton?s neuroma is 8 to 10 times greater in women than in men.
Morton?s neuroma occurs as the nerve passes under the ligament connecting the toe bones (metatarsals) in the forefoot. Morton?s neuroma most frequently develops between the third and fourth toes, usually in response to irritation, trauma or excessive pressure. The incidence of Morton?s neuroma is 8 to 10 times greater in women than in men.
Causes
Morton's neuroma develops for several reasons. The primary reason is wearing narrow toe-box shoes, which compress the metatarsal heads. Certain anatomical factors also make nerve compression more likely with the narrow toe box shoes. In some people fibers, the medial and lateral plantar nerves converge close to the heads of the third and fourth metatarsals. This junction creates a larger nerve structure between the metatarsal heads making it more vulnerable to compression.
Symptoms
If you have a Morton's neuroma, you will probably have one or more of these symptoms. Tingling, burning, or numbness. A feeling that something is inside the ball of the foot, or your sock is bunched up. Pain that is relieved by removing your shoes. A Morton's Neuroma often develops gradually. At first the symptoms may occur only occasionally, when wearing narrower shoes or performing certain activities. The symptoms may go away temporarily by massaging the foot or by avoiding aggravating shoes or activities. Over time the symptoms progressively worsen and may persist for several days or weeks. The symptoms become more intense as the neuroma enlarges and the temporary changes in the nerve become permanent.
Diagnosis
Morton?s neuroma can be identified during a physical exam, after pressing on the bottom of the foot. This maneuver usually reproduces the patient?s pain. MRI and ultrasound are imaging studiesthat can demonstrate the presence of the neuroma. An x-ray may also be ordered to make sure no other issues exist in the foot. A local anesthetic injection along the neuroma may temporarily abolish the pain, and help confirm the diagnosis.
Non Surgical Treatment
The most important factor in the treatment of Morton's neuroma is changing footwear. Sometimes a cushioned dome pad can be worn inside the shoe and this helps spread the metatarsal heads and decrease pressure on the nerve. There are other products that can be worn between the toes with certain types of shoes or when the client is barefoot. These toe spacers will help reverse biomechanical patterns that aggravate the nerve compression. Massage can be helpful, but should not be performed with deep pressure between the metatarsal heads. Additional pressure in this region can aggravate the nerve compression and prolong the pathology.
Surgical Treatment
Patients are commonly offered surgery known as neurectomy, which involves removing the affected piece of nerve tissue. Postoperative scar tissue formation (known as stump neuroma) can occur in approximately 20%-30% of cases, causing a return of neuroma symptoms. Neurectomy can be performed using one of two general methods. Making the incision from the dorsal side (the top of the foot) is the more common method but requires cutting the deep transverse metatarsal ligament that connects the 3rd and 4th metatarsals in order to access the nerve beneath it. This results in exaggerated postoperative splaying of the 3rd and 4th digits (toes) due to the loss of the supporting ligamentous structure. This has aesthetic concerns for some patients and possible though unquantified long-term implications for foot structure and health. Alternatively, making the incision from the ventral side (the sole of the foot) allows more direct access to the affected nerve without cutting other structures. However, this approach requires a greater post-operative recovery time where the patient must avoid weight bearing on the affected foot because the ventral aspect of the foot is more highly enervated and impacted by pressure when standing. It also has an increased risk that scar tissue will form in a location that causes ongoing pain.
.jpg) Morton?s neuroma occurs as the nerve passes under the ligament connecting the toe bones (metatarsals) in the forefoot. Morton?s neuroma most frequently develops between the third and fourth toes, usually in response to irritation, trauma or excessive pressure. The incidence of Morton?s neuroma is 8 to 10 times greater in women than in men.
Morton?s neuroma occurs as the nerve passes under the ligament connecting the toe bones (metatarsals) in the forefoot. Morton?s neuroma most frequently develops between the third and fourth toes, usually in response to irritation, trauma or excessive pressure. The incidence of Morton?s neuroma is 8 to 10 times greater in women than in men.Causes
Morton's neuroma develops for several reasons. The primary reason is wearing narrow toe-box shoes, which compress the metatarsal heads. Certain anatomical factors also make nerve compression more likely with the narrow toe box shoes. In some people fibers, the medial and lateral plantar nerves converge close to the heads of the third and fourth metatarsals. This junction creates a larger nerve structure between the metatarsal heads making it more vulnerable to compression.
Symptoms
If you have a Morton's neuroma, you will probably have one or more of these symptoms. Tingling, burning, or numbness. A feeling that something is inside the ball of the foot, or your sock is bunched up. Pain that is relieved by removing your shoes. A Morton's Neuroma often develops gradually. At first the symptoms may occur only occasionally, when wearing narrower shoes or performing certain activities. The symptoms may go away temporarily by massaging the foot or by avoiding aggravating shoes or activities. Over time the symptoms progressively worsen and may persist for several days or weeks. The symptoms become more intense as the neuroma enlarges and the temporary changes in the nerve become permanent.
Diagnosis
Morton?s neuroma can be identified during a physical exam, after pressing on the bottom of the foot. This maneuver usually reproduces the patient?s pain. MRI and ultrasound are imaging studiesthat can demonstrate the presence of the neuroma. An x-ray may also be ordered to make sure no other issues exist in the foot. A local anesthetic injection along the neuroma may temporarily abolish the pain, and help confirm the diagnosis.
Non Surgical Treatment
The most important factor in the treatment of Morton's neuroma is changing footwear. Sometimes a cushioned dome pad can be worn inside the shoe and this helps spread the metatarsal heads and decrease pressure on the nerve. There are other products that can be worn between the toes with certain types of shoes or when the client is barefoot. These toe spacers will help reverse biomechanical patterns that aggravate the nerve compression. Massage can be helpful, but should not be performed with deep pressure between the metatarsal heads. Additional pressure in this region can aggravate the nerve compression and prolong the pathology.

Surgical Treatment
Patients are commonly offered surgery known as neurectomy, which involves removing the affected piece of nerve tissue. Postoperative scar tissue formation (known as stump neuroma) can occur in approximately 20%-30% of cases, causing a return of neuroma symptoms. Neurectomy can be performed using one of two general methods. Making the incision from the dorsal side (the top of the foot) is the more common method but requires cutting the deep transverse metatarsal ligament that connects the 3rd and 4th metatarsals in order to access the nerve beneath it. This results in exaggerated postoperative splaying of the 3rd and 4th digits (toes) due to the loss of the supporting ligamentous structure. This has aesthetic concerns for some patients and possible though unquantified long-term implications for foot structure and health. Alternatively, making the incision from the ventral side (the sole of the foot) allows more direct access to the affected nerve without cutting other structures. However, this approach requires a greater post-operative recovery time where the patient must avoid weight bearing on the affected foot because the ventral aspect of the foot is more highly enervated and impacted by pressure when standing. It also has an increased risk that scar tissue will form in a location that causes ongoing pain.
Are Shoe Lifts The Ideal Solution To Leg Length Difference
There are actually not one but two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital indicates that you are born with it. One leg is structurally shorter in comparison to the other. Through developmental stages of aging, the brain senses the stride pattern and recognizes some variance. The entire body typically adapts by tilting one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of under a quarter inch is not very abnormal, require Shoe Lifts to compensate and generally does not have a profound effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes largely undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this condition is easily remedied, and can eliminate a number of incidents of upper back pain.
Therapy for leg length inequality typically consists of Shoe Lifts. These are very inexpensive, commonly being below twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Mid back pain is the most common ailment affecting men and women today. Over 80 million people suffer from back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem that costs businesses vast amounts of money every year as a result of time lost and productivity. Fresh and better treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of minimizing the economic influence this issue causes.

People from all corners of the world suffer the pain of foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these types of cases Shoe Lifts might be of very useful. The lifts are capable of easing any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by many specialist orthopaedic practitioners".
So that you can support the body in a nicely balanced fashion, your feet have got a critical job to play. Irrespective of that, it is often the most neglected zone in the human body. Some people have flat-feet meaning there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This causes other parts of the body such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that correct posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes largely undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this condition is easily remedied, and can eliminate a number of incidents of upper back pain.
Therapy for leg length inequality typically consists of Shoe Lifts. These are very inexpensive, commonly being below twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Mid back pain is the most common ailment affecting men and women today. Over 80 million people suffer from back pain at some point in their life. It's a problem that costs businesses vast amounts of money every year as a result of time lost and productivity. Fresh and better treatment methods are continually sought after in the hope of minimizing the economic influence this issue causes.

People from all corners of the world suffer the pain of foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these types of cases Shoe Lifts might be of very useful. The lifts are capable of easing any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by many specialist orthopaedic practitioners".
So that you can support the body in a nicely balanced fashion, your feet have got a critical job to play. Irrespective of that, it is often the most neglected zone in the human body. Some people have flat-feet meaning there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This causes other parts of the body such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that correct posture and balance are restored.
What Is Inferior Calcaneal Spur
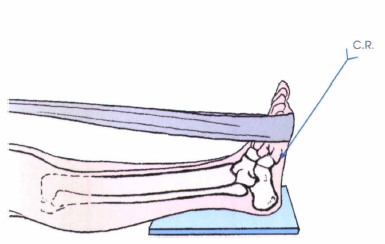
Overview
A heel spur is a calcium deposit on the underside of the heel bone, often caused by strain on foot muscles and ligaments. Heel spurs are common among athletes but also tend to develop as we age, as flexibility decreases. Heel spurs can be painful when associated with plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the connective tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot and connects the heel bone to the ball of the foot.
If left untreated, the mild aches associated with this condition can evolve into chronic pain. And as you try to compensate for the pain, your gait may change, which could impact your knee, hip and back.
Causes
One frequent cause of heel spurs is an abnormal motion and mal-alignment of the foot called pronation. For the foot to function properly, a certain degree of pronation is required. This motion is defined as an inward action of the foot, with dropping of the inside arch as one plants the heel and advances the weight distribution to the toes during walking. When foot pronation becomes extreme from the foot turning in and dropping beyond the normal limit, a condition known as excessive pronation creates a mechanical problem in the foot. In some cases the sole or bottom of the foot flattens and becomes unstable because of this excess pronation, especially during critical times of walking and athletic activities. The portion of the plantar fascia attached into the heel bone or calcaneous begins to stretch and pull away from the heel bone.

Symptoms
The vast majority of people who have heel spurs feel the asscociated pain during their first steps in the morning. The pain is quite intense and felt either the bottom or front of the heel bone. Typically, the sharp pain diminishes after being up for a while but continues as a dull ache. The pain characteristically returns when first standing up after sitting for long periods.
Diagnosis
A thorough history and physical exam is always necessary for the proper diagnosis of heel spurs and other foot conditions. X rays of the heel area are helpful, as excess bone production will be visible.
Non Surgical Treatment
If pain and other symptoms of inflammation-redness, swelling, heat-persist, you should limit normal daily activities and contact a doctor of podiatric medicine. The podiatric physician will examine the area and may perform diagnostic X-rays to rule out problems of the bone. Early treatment might involve oral or injectable anti-inflammatory medication, exercise and shoe recommendations, taping or strapping, or use of shoe inserts or orthotic devices. Taping or strapping supports the foot, placing stressed muscles and tendons in a physiologically restful state. Physical therapy may be used in conjunction with such treatments. A functional orthotic device may be prescribed for correcting biomechanical imbalance, controlling excessive pronation, and supporting of the ligaments and tendons attaching to the heel bone. It will effectively treat the majority of heel and arch pain without the need for surgery. Only a relatively few cases of heel pain require more advanced treatments or surgery. If surgery is necessary, it may involve the release of the plantar fascia, removal of a spur, removal of a bursa, or removal of a neuroma or other soft-tissue growth.
Surgical Treatment
Though conservative treatments for heel spurs work most of the time, there are some cases where we need to take your treatment to the next level. Luckily, with today?s technologies, you can still often avoid surgery. Some of the advanced technologies to treat a Heel Spur are Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy. Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy (also known as PRP) is one of several regenerative medicine techniques that University Foot and Ankle Institute has helped bring to foot and ankle care. This amazing in-office procedure allows the growth factors in the blood to be used to actually begin the healing process again long after your body has given up on healing the area. Heel Pain Shockwave Therapy. Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive procedure done in the office that allows for new blood to get to the region of fascia damage and help with healing. Results have been excellent with more than 70 percent of patients getting relief with only one treatment. Topaz for Heal Spurs and pain. Another minimally invasive technology technique is called Coblation Surgery using a Topaz probe. This minimally invasive procedure involves controlled heating of multiple tiny needles that are inserted through the skin and into the plantar fascia. This process, like PRP and Shockwave therapy, irritates the fascia enough to turn a chronic problem back into an acute problem, greatly increasing the chances of healing. Heel Spur Surgery. Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy is one surgical procedure that we consider to release the tight fascia. University Foot and Ankle Institute has perfected an endoscopic (camera guided) approach for fascia release to allow rapid healing and limited downtime with minimal pain.
Ways To Protect Against Heel Spur
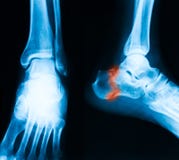
Overview
The two most common causes of pain in the bottom of the heel, the arch, or both the heel and the arch, are heel spurs and plantar fasciitis. A Heel Spur is a piece of calcium or bone that sticks out from the bottom of the heel bone, and lies within the fibers of the plantar fascia. When walking, the spur digs into the plantar fascia and causes small micro-tears in the plantar fascia. This produces inflammation and pain in the heel, which at times may radiate into the arch.
Causes
The calcaneal spur is seen most often in persons over the age of 40. The condition can also be associated with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, poor circulation of the blood and other degenerative diseases. Men and women are equally likely to have them.
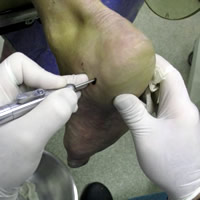
Symptoms
Most heel spurs cause no symptoms and may go undetected for years. If they cause no pain or discomfort, they require no treatment. Occasionally, a bone spur will break off from the larger bone, becoming a ?loose body?, floating in a joint or embedding itself in the lining of the joint. This can cause pain and intermittent locking of the joint. In the case of heel spurs, sharp pain and discomfort is felt on the bottom of the foot or heel.
Diagnosis
Because the diagnosis of heel spurs can be confused with tarsal tunnel syndrome (as described earlier), most surgeons advocate performing a tarsal tunnel release (or at least a partial tarsal tunnel release) along with the plantar fascia release. This surgery is about 80percent successful in relieving pain in the small group of patients who do not improve with conservative treatments.
Non Surgical Treatment
Podiatric Care for heel spur syndrome may involve keeping the fascia stretched out by performing exercises. Your doctor may also suggest for you to be seen by a physical therapist. You probably will be advised on the best shoes to wear or some inserts for your shoes. Your podiatrist may suggest that a custom made orthotic be made to allow your foot to function in the most ideal way especially if you have excessive pronation. A heel lift may be used if you have a leg length discrepancy. Medical treatment may include anti-inflammatory oral medications or an injection of medication and local anesthetic to reduce the swelling and decrease pain. If a bursitis is present the medication may greatly improve the symptoms. Your podiatric physician may also recommend a surgical procedure to actually fix the structural problem of your foot.
Surgical Treatment
Sometimes bone spurs can be surgically removed or an operation to loosen the fascia, called a plantar fascia release can be performed. This surgery is about 80 percent effective in the small group of individuals who do not have relief with conservative treatment, but symptoms may return if preventative measures (wearing proper footwear, shoe inserts, stretching, etc) are not maintained.
Prevention
Use orthotic inserts. You can purchase orthotics over the counter, or you can have orthotics specially fitted by your podiatrist. Try 1 of these options. Heel cups. These inserts will help to align the bones in your foot and to cushion your heel. Check your skin for blisters when you first start using heel cups. Also, your feet may sweat more with a heel cup, so change your socks and shoes often. Insoles. While you can pick up generic insoles at a drugstore, you may have more luck if you go to a store that sells athletic shoes. Push on the arch to make sure that it doesn't collapse. If your insoles help but could use a little work, you can take them to a podiatrist to get them customized. Custom orthotics. A podiatrist can make a cast of your foot and provide you with custom-made orthotics. These may be more expensive, but they are made of materials specifically designed for your needs, and they can last up to 5 years if your podiatrist refurbishes them every 1 or 2 years. To find a podiatrist near you, look at the Web page for the American Academy of Podiatric Sports Medicine. Dynamic Insoles. Lack of elasticity in plantar fascia in the foot is for most people the real problem. If there is poor elasticity in the lengthwise tendons in the foot (plantar fascia) in relation to a person's general condition, only a small additional strain is required for the pull on the tendons to cause damage to the tissues connecting the tendons to the heel bone. This will generate an inflamed condition called Plantar Fasciitis.